An atom is made up of subatomic particles called protons, neutrons and electrons.
- Protons are positively charged particles;
- Neutrons have no electrical charge;
- Electrons are negatively charged particles.
As shown in Figure 1 below, an atom consists of an inner nucleus with protons and neutrons with electrons located outside the nucleus.
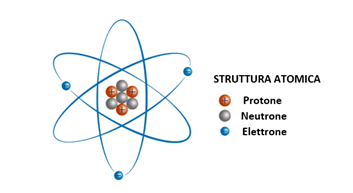
Figure 1 – Representation of the atomic structure.
All the positive charge is concentrated in the center of the atom, while the negative charge is distributed externally. The role of the neutron is to increase the distance between the protons and prevent proton-proton repulsive interactions from destabilizing the entire structure.
The masses of subatomic particles are extremely small.
- Proton mass: 1.673×10−27 kg
- Neutron mass: 1,675×10−27 kg
- Electron mass: 9,109×10−31 kg
The mass of the electron is nearly 2,000 times smaller than that of the proton and neutron, which is why it can be considered negligible.
Even the charges of subatomic particles are significantly small.
- Proton charge: + 1.602×10−19 C
- Neutron charge: 0 C
- Electron charge: – 1.602×10−19 C
The charge of a proton is equal to the charge of an electron, though with the opposite sign. The overall charge of the atom is neutral, meaning the positive charge of the nucleus is balanced by the negative charge of the electrons.
Since the charge of a proton is equal to the charge of an electron, it’s easy to deduce:
IN AN ATOM THE NUMBER OF PROTONS IS EQUAL TO THE NUMBER OF ELECTRONS.
ATOMIC NUMBER AND MASS NUMBER
Atoms can be identified by two types of numbers:
- ATOMIC NUMBER (Z) which represents the number of protons;
- MASS NUMBER (A) which represents the sum of protons and neutrons.
The difference between the atomic number (Z) and the mass number (A) gives the number of neutrons.
As shown in Figure 2, a chemical element is described by two numbers: the atomic number (Z), which is listed in the lower left, and the mass number (A), which is listed in the upper left.
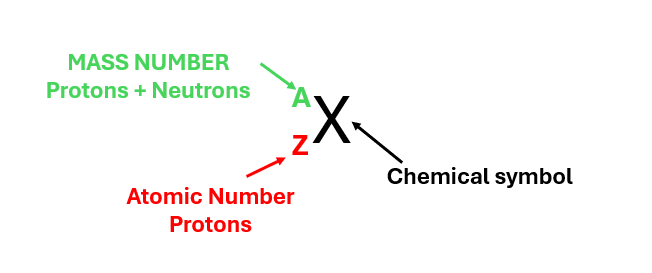
Figure 2 – Representation of a chemical element.
KEY POINTS:
- MASS NUMBER (protons + neutrons) is always listed in the upper left;
- ATOMIC NUMBER (protons) is always listed in the lower left;
- In an atom the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons;
- The number of neutrons is obtained by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number.
SOLVED EXERCISE:
Find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the following atom:
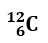
- Atomic number, reported in the lower left, represents the number of protons. p+= 6
- The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. e–= 6
- (Mass number – Atomic Number)= Number of neutrons. n = 12-6 = 6
SOLUTION:
p+= 6;
n = 6;
e–= 6
