An explosion is a phenomenon capable of releasing a huge amount of energy in a very short time, primarily as heat and electromagnetic radiation.

Besides the release of a huge amount of energy, an explosion is accompanied by a rapid increase in pressure due to the release of high-pressure gases.
These gases push and compress the surrounding atmosphere, which in turn pushes and compresses air volumes further away. This results in the formation of a high-pressure wave that propagates at a certain speed from the point of the explosion.
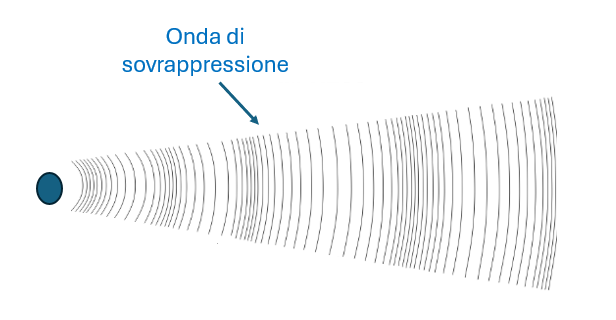
If the speed of the high-pressure wave is below the speed of sound, the explosion is called a deflagration (subsonic wave).
If the speed of the high-pressure wave is greater than the speed of sound, the explosion is called a detonation (supersonic wave).
